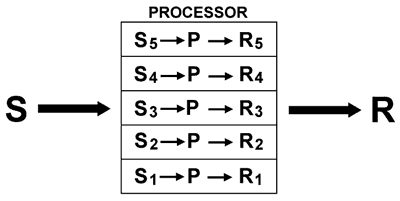
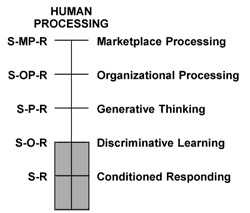
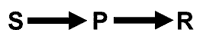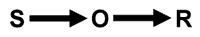“No Child Left Behind” is legislation that leaves every child behind. It simply does not prepare the 21st century learners for the world they must address. This is a world that requires Generative Thinking Skills. This is legislation that delivers only conditional responding skills.
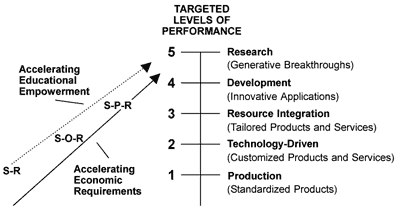
Generative Thinking Architecture
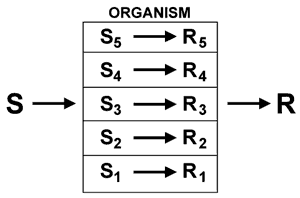
The mission of Generative Thinking is to create responses where there were none. Indeed, the precise definition of Generative Thinking is as follows:
To create responses that the stimuli were not intended to elicit.
In other words, thinking generates new and more productive responses to the continuously-changing stimulus conditions of our time.
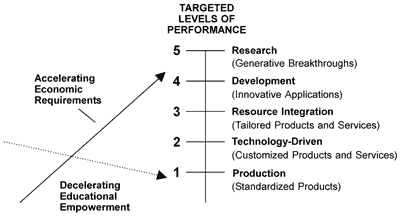
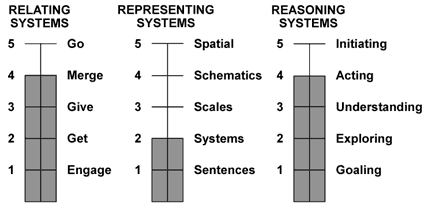
There are three sets of processing systems involved in Generative Thinking:
- Relating to elicit images;
- Representing to develop new images;
- Reasoning to generate or create the most productive images.
These processing systems are transformed into thinking skills in systematic training programs.
Relating Skills
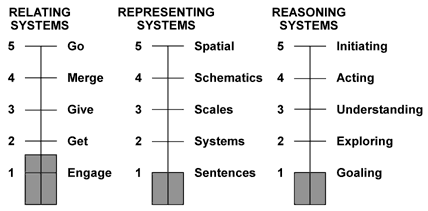
The first set of processing skills emphasizes “Relating to Elicit Images.” This means that we employ our “Information Communication Skills” to obtain images of any phenomena or circumstances (See Figure 4):
- Responding accurately to get others’ images;
- Initiating operationally to give our images;
- Negotiating merged images of phenomena.
Relating is the essential beginning phase in Generative Thinking because it yields images of conceptual information with which to reason.

Figure 4. Relating to Elicit Images
Representing Skills
The second set of processing skills emphasizes “Representing to Develop New Images.” This means that we employ our “Information Representing Skills” to develop new images of any phenomena or circumstances (See Figure 5):
- Sentences or conceptual levels of information;
- Systems or operational levels of information;
- Schematics or dimensional levels of information.
Relating is the necessary transitional phase in processing because it yields us images of operational information with which to reason.
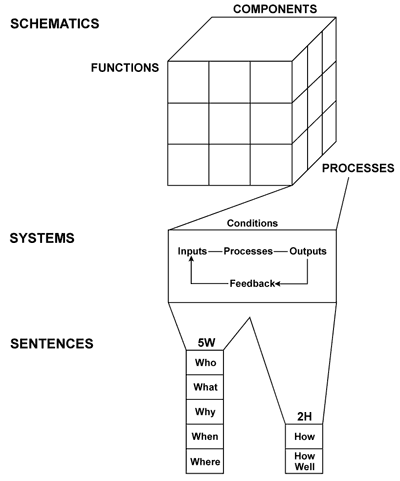
Figure 5. Representing to Develop New Images
Reasoning Skills
The third and culminating set of processing skills emphasize “Reasoning to Generate the Most Productive Images.” This means that we employ “Information Reasoning Skills” to generate newer and more productive images of any phenomena or circumstance (See Figure 6):
- Exploring by expanding images of information;
- Understanding by narrowing images of information;
- Acting by defining information objectives.
Reasoning is the culminating phase in Generative Thinking because it yields us new and more productive information objectives for acting.
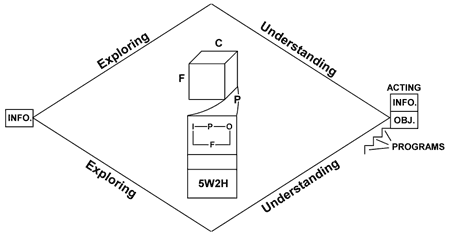
Figure 6. Reasoning to Generate More Productive Images
To sum, the three phases of Generative Thinking are “nested” or “housed” in generative thinking:
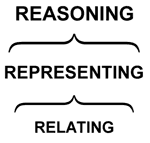
Figure 7. The Phases of Generative Thinking
Relating elicits the images that Representing develops and Reasoning processes generatively. Systematically trained and implemented, Generative Thinking creates totally new images of information with which we can create our own changeable destinies.
In summary, perhaps the most grievous harm of “No Child Left Behind” is this: because we actually “swallowed the bait—hook, line and sinker,” we got “stuck” with the “switch, hook line and stinker”—the empty promises that we made and “kept” to our children.
We placed the students in “double jeopardy.” Those who were initially “held back” by adults, were now systematically “held back” by their teachers, all in the name of “leaving no child behind.”
In transition, the best thing that can be said about “No Child Left Behind” is that children are learning the wrong things. The worst thing that could be said is that they are getting “dumber” as they achieve higher standards.
Our conclusion may be best represented by the question asked by the “Prime Mover” of this legislation:
“Is the children learning?”